Smart Water Filtration: How Technology Is Shaping Safe and Sustainable Water
Why Filtration Matters in Modern Water Supply
Access to clean, safe water is essential for communities, industries, and the environment. Recent high-profile water safety incidents have underscored the crucial role of advanced filtration systems. Organizations, regulatory agencies, and individuals now place greater focus on ensuring water sources meet strict safety standards, recognizing that water quality is non-negotiable for health, agriculture, manufacturing, and everyday life. This urgency is especially apparent for regions managing complex needs, such as those with large-scale facilities that rely on industrial-grade water filtration systems in Maryland, where reliability, scalability, and compliance are mission-critical.
The drive for more resilient water supplies has sparked innovation, bringing high-efficiency filtration solutions to homes and highly specialized, sensor-driven technologies to factories and public utilities. These advances have not only raised the baseline for water cleanliness but also forged new pathways to sustainability by reducing waste, energy use, and environmental impact. As climate challenges, population growth, and changing regulations increase pressure on water sources, investing in robust filtration is an investment in public safety and long-term resilience.
What Are the Most Common Water Contaminants?
Clean drinking water is often compromised by a complex array of contaminants—biological, chemical, and physical. Pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites, pose infectious risks, while trace metals like lead or arsenic can result in long-term health consequences. Modern water systems also confront pollutants such as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), nitrates, pesticides, and microplastics, many of which resist conventional treatment methods.
Types of Filtration Systems: From Sand to Smart Sensors
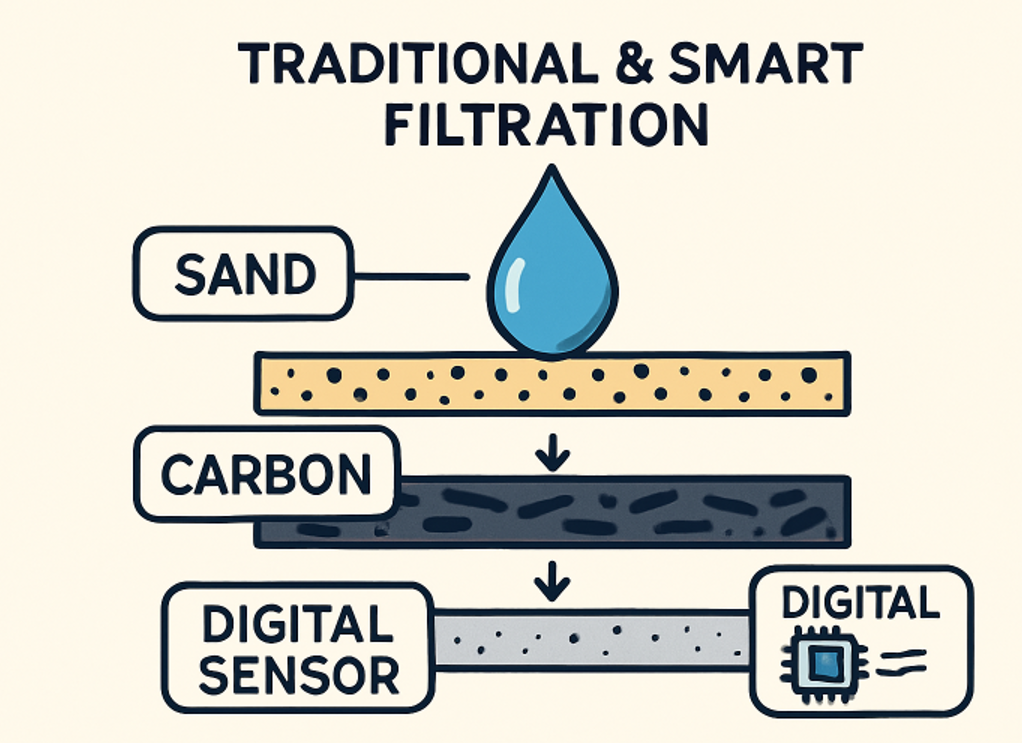
Water filtration technologies provide a range of solutions, each tailored to address distinct challenges. Time-honored approaches, such as sand and activated carbon filters, effectively capture particulates and neutralize chlorine or organic chemicals. Reverse osmosis, nanofiltration, and ultraviolet (UV) disinfection push the envelope, eliminating microscopic contaminants, dissolved solids, bacteria, and even some viruses.
In recent years, smart filtration systems have gained popularity, particularly among large institutions and tech-savvy homeowners. These systems leverage integrated sensors and real-time data analytics to detect changes in water quality, signal maintenance needs, and minimize risks before they escalate. The fusion of traditional methods and sensor-equipped systems is rapidly transforming water safety into a more proactive, transparent, and user-friendly endeavor.
Technology Trends Transforming Water Filtration
Technological innovation remains at the heart of the water filtration revolution. Smart home platforms now offer connected filtration systems, allowing users to monitor water quality and receive alerts via apps when filter changes or services are due. On an industrial scale, sophisticated analytics, remote monitoring, and artificial intelligence enable operators to manage complex processes and identify issues before they impact end users or production lines.
Material science breakthroughs, such as graphene-enhanced membranes and bio-based filter media, promise unprecedented filtration efficiency while reducing waste and operational costs. These advances are turning water treatment into a predictive science—directing attention to maintenance, optimization, and emergency response at precisely the right moments.
Key Benefits for Health and the Environment
Advanced water filtration delivers tangible benefits well beyond the tap. Effective filtration reduces the incidence of waterborne diseases, safeguarding public health by controlling the spread of harmful microorganisms and mitigating the risk of chronic exposure to toxins. On the environmental front, sustainable filtration technologies help reduce plastic use by minimizing reliance on bottled water, and eco-friendly systems are designed to minimize water and energy waste during operation.
For municipalities and industries alike, upgrading to new filtration systems can mean substantial savings in resources and a smaller ecological footprint—a necessary evolution as water scarcity and contamination remain global threats. Access to reliable, high-quality water is also key to supporting biodiversity and maintaining healthy ecosystems downstream.
Current Guidelines and Regulatory Developments
Water quality is closely regulated around the world. Agencies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and World Health Organization (WHO) continually revise standards to reflect the latest scientific knowledge and public demand for transparency. Recent attention has focused on emerging contaminants—such as pharmaceuticals, hormones, and microplastics—which are often not addressed by legacy standards.
Adhering to current guidelines and proactively incorporating technology that exceeds basic requirements positions suppliers and consumers to weather both regulatory shifts and unforeseen risks.
How to Choose the Right Filtration System
- Assess your source: Determine whether your water comes from a municipal supply or a private well—each presents unique risks and requirements.
- Test for contaminants: Perform a thorough water analysis to identify microbial, mineral, or chemical pollutants.
- Match technology to needs: Use activated carbon for chlorine and organic removal or reverse osmosis for addressing dissolved solids, lead, and salts.
- Consider maintenance: Factor in upkeep; more advanced systems may need periodic servicing or sensor recalibration.
For complex or high-risk environments, it’s advisable to partner with a water quality expert. Their insights help ensure that selected solutions are both practical and efficient for the application and region.
See also: Turf Laying Services: The Key to a Lush, Healthy Lawn
What’s Next: Future Innovations in Water Filtration
The next era in water filtration will leverage technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and sustainable materials. Emerging solutions include real-time contamination alerts powered by remote sensors, filters that self-diagnose and report, and membrane materials with higher yields and longer lifespans. Boundaries between residential, municipal, and industrial technologies will continue to blur, ensuring broad access to state-of-the-art safety features and more sustainable designs.
Ongoing pilot programs around the globe are testing new systems designed to react swiftly to contamination, reduce downtime, and provide users with unprecedented transparency into what’s in their water. Continuous learning from these projects is vital for staying ahead of threats and making informed decisions in both domestic and commercial contexts.
Conclusion
The convergence of traditional filtration wisdom with emerging smart technologies equips society to better tackle the water quality challenges of today and tomorrow. By choosing and maintaining advanced filtration systems, communities, businesses, and individuals ensure safer water, protect public health, and contribute to a more sustainable planet. Remaining informed and adaptable is the best way to keep water clean—and plentiful—for future generations.